Spring Security 6.4 introduces native OAuth2 support for the RestClient, making it easier than ever to secure your service-to-service communications. If you've been using RestClient since its introduction in Spring Framework 6.1, you'll appreciate this streamlined approach to OAuth2 integration. Let's explore how this new feature simplifies secure API interactions.
The Evolution of HTTP Clients in Spring
The RestClient, introduced in Spring Framework 6.1, provided developers with a fluent, synchronous API for HTTP communications. While it quickly gained popularity for its clean interface and lack of reactive dependencies, implementing OAuth2 security required custom solutions. Spring Security 6.4 addresses this gap with built-in OAuth2 support.
Understanding the Architecture
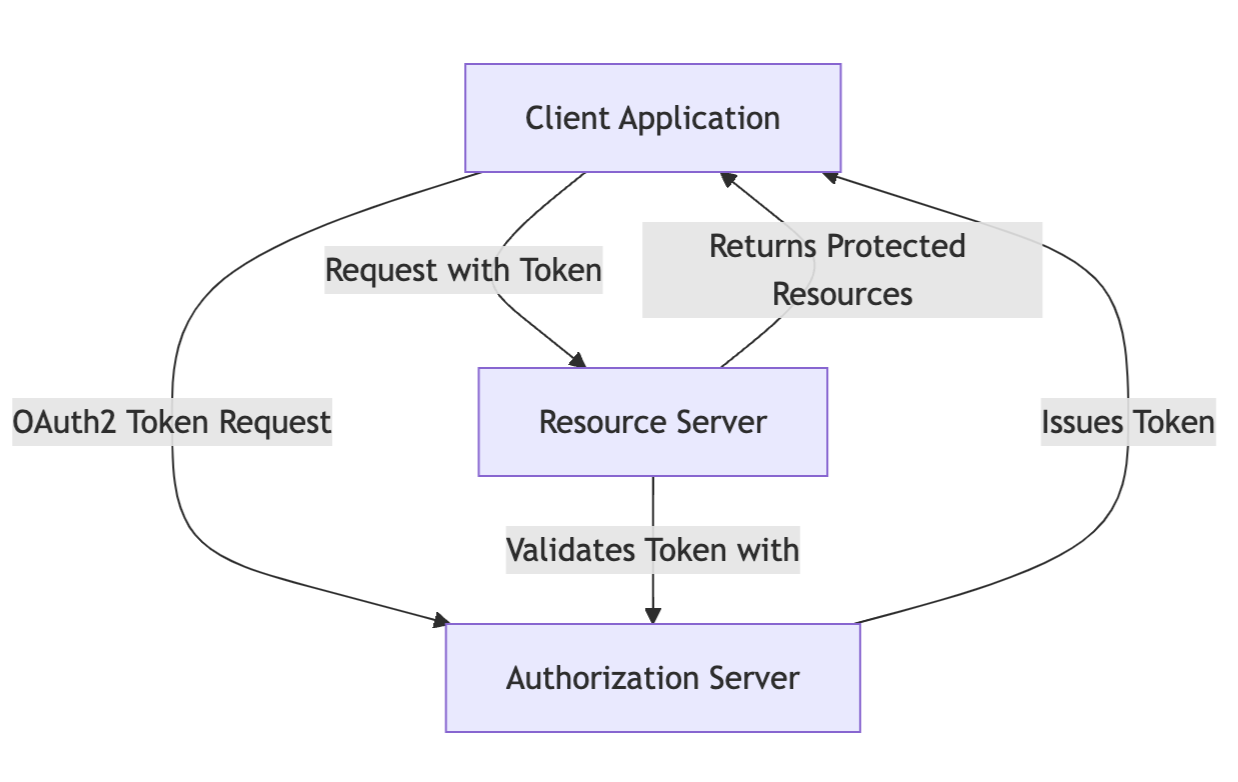
Before diving into the implementation, let's understand the key components in a typical OAuth2 setup:
- Authorization Server - Issues and validates OAuth2 tokens
- Resource Server - Hosts protected resources requiring OAuth2 authentication
- Client Application - Makes authenticated requests using OAuth2 tokens
Here's how these components interact in a typical flow:
- The client requests an access token from the Authorization Server
- The Authorization Server validates credentials and returns a token
- The client includes this token when requesting protected resources
- The Resource Server validates the token before serving the request
Implementing OAuth2 with RestClient
Let's implement this using Spring Security 6.4's new RestClient OAuth2 support. We'll create a client application that securely accesses protected resources.
Client Configuration
First, configure your OAuth2 client properties:
spring:
security:
oauth2:
client:
registration:
golf-client:
provider: spring
client-id: golf-client
client-secret: golf-secret
authorization-grant-type: client_credentials
scope: read
provider:
spring:
token-uri: http://localhost:9000/oauth2/token
RestClient Setup
Create a RestClient bean with OAuth2 support:
@Configuration
public class ClientConfig {
@Bean
RestClient restClient(RestClient.Builder builder, OAuth2ClientHttpRequestInterceptor interceptor) {
return builder
.baseUrl("http://localhost:8081")
.requestInterceptor(interceptor)
.build();
}
}
The new OAuth2ClientHttpRequestInterceptor handles token acquisition and request enhancement automatically.
Making Authenticated Requests
Use the attributes() method to specify OAuth2 details:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class LessonsController {
private final RestClient restClient;
public LessonsController(RestClient restClient) {
this.restClient = restClient;
}
@GetMapping("/lessons")
public List<Lesson> getLessons() {
return restClient.get()
.uri("/lessons")
.attributes(OAuth2ClientAttributesUtils.clientRegistrationId("golf-client"))
.retrieve()
.body(new ParameterizedTypeReference<>() {});
}
}
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
- Missing Security Configuration
Without proper security configuration, you might get redirected to form login. Add this configuration:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
return http
.formLogin(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth.anyRequest().permitAll())
.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.build();
}
}
- Token Validation Issues
Ensure your Resource Server is configured to validate tokens:
spring:
security:
oauth2:
resourceserver:
jwt:
issuer-uri: http://localhost:9000
Testing Your Implementation
Here's a simple test to verify your OAuth2 integration:
@SpringBootTest
class LessonsControllerTest {
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@Test
void whenRequestingLessons_thenReturnsAuthorizedResponse() {
ResponseEntity<List<Lesson>> response = restTemplate.exchange(
"/api/lessons",
HttpMethod.GET,
null,
new ParameterizedTypeReference<>() {}
);
assertThat(response.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
assertThat(response.getBody()).isNotEmpty();
}
}
Conclusion
Spring Security 6.4's RestClient OAuth2 support significantly simplifies secure service-to-service communication. The integration feels natural and follows Spring's philosophy of convention over configuration.
For developers currently using custom OAuth2 solutions with RestClient, migrating to this official support offers several advantages:
- Reduced boilerplate code`
- Automatic token management`
- Consistent security configuration
- Better integration with Spring Security's features
Ready to try it yourself? Start by upgrading to Spring Security 6.4 and following the implementation pattern shown above. Remember to check the official Spring documentation for the most up-to-date details and best practices.
Have you already implemented OAuth2 with RestClient? How does this new approach compare to your current solution? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!
Related Articles
Spring Security 7 Multi-Factor Authentication: Complete Tutorial with @EnableMultiFactorAuthentication
Learn how to implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) in Spring Boot 4 using Spring Security 7's new @EnableMultiFactorAuthentication annotation. Step-by-step tutorial with one-time token login and custom PIN codes.
Building a Spring Security Login Form with JTE
Learn how to create a secure login form using Spring Security and JTE (Java Template Engine) with support for both traditional authentication and OAuth2 providers.
What's new in Spring Security 6
In this article we will discuss the new features of Spring Security 6 and create a new Spring Boot 3 project together.