Welcome back, everyone. Dan Vega here, and today we are going to dive into the fascinating world of Ollama. But you might be wondering, what exactly is Ollama, and why should you care about it? Well, let's break it down.
Introduction to Ollama
Ollama is a tool that allows us to get up and running with large language models (LLMs) on our local machines. It's part of the wave of new technology that includes models like the newly open-sourced Llama 3.1 from Meta, Mistral, and many more. The big question on your mind might be: why would anyone want to run an LLM locally?
Why Run Large Language Models Locally?
In my opinion here are two primary reasons for doing this: cost and security.
Cost Efficiency
When you're using large language models from providers like OpenAI's GPT-4, Google Gemini, etc., there are costs involved. While prototyping or developing an MVP might not incur substantial costs, you will eventually need to put a credit card on file for continued use.

Security
For enterprises or organizations dealing with private or sensitive documents, running an LLM locally can be a game-changer. It ensures that your data doesn't have to leave your secure environment, making it perfect for tasks involving confidential information.
Additional Reasons to run an LLM Locally
- Offline access: Local LLMs can operate without an internet connection, which is beneficial in areas with poor connectivity or in situations where internet access is restricted.
- Lower latency: Local models can provide faster response times since there's no need to send requests to and receive responses from a remote server.
- Customization and fine-tuning: Local deployment allows for easier customization and fine-tuning of the model to specific use cases or domains.
- Regulatory compliance: For industries with strict data regulations, local LLMs can help ensure compliance by keeping data within controlled environments.
Getting Started with Ollama
Here's how you can get started with Ollama and make your development experience smoother.
Download and Installation
First, head over to Ollama's website and download the necessary files. Ollama is compatible with macOS, Linux, and Windows. For this guide, I will be using macOS.
Once you've downloaded it, follow the installation steps. This will install a Command Line Interface (CLI) on your system.
Selecting a Model
After the CLI is up and running, you’ll need to choose a model. Ollama supports various models, each optimized for different tasks. For instance, you might find models optimized for conversational interactions, long-context tasks, and more.
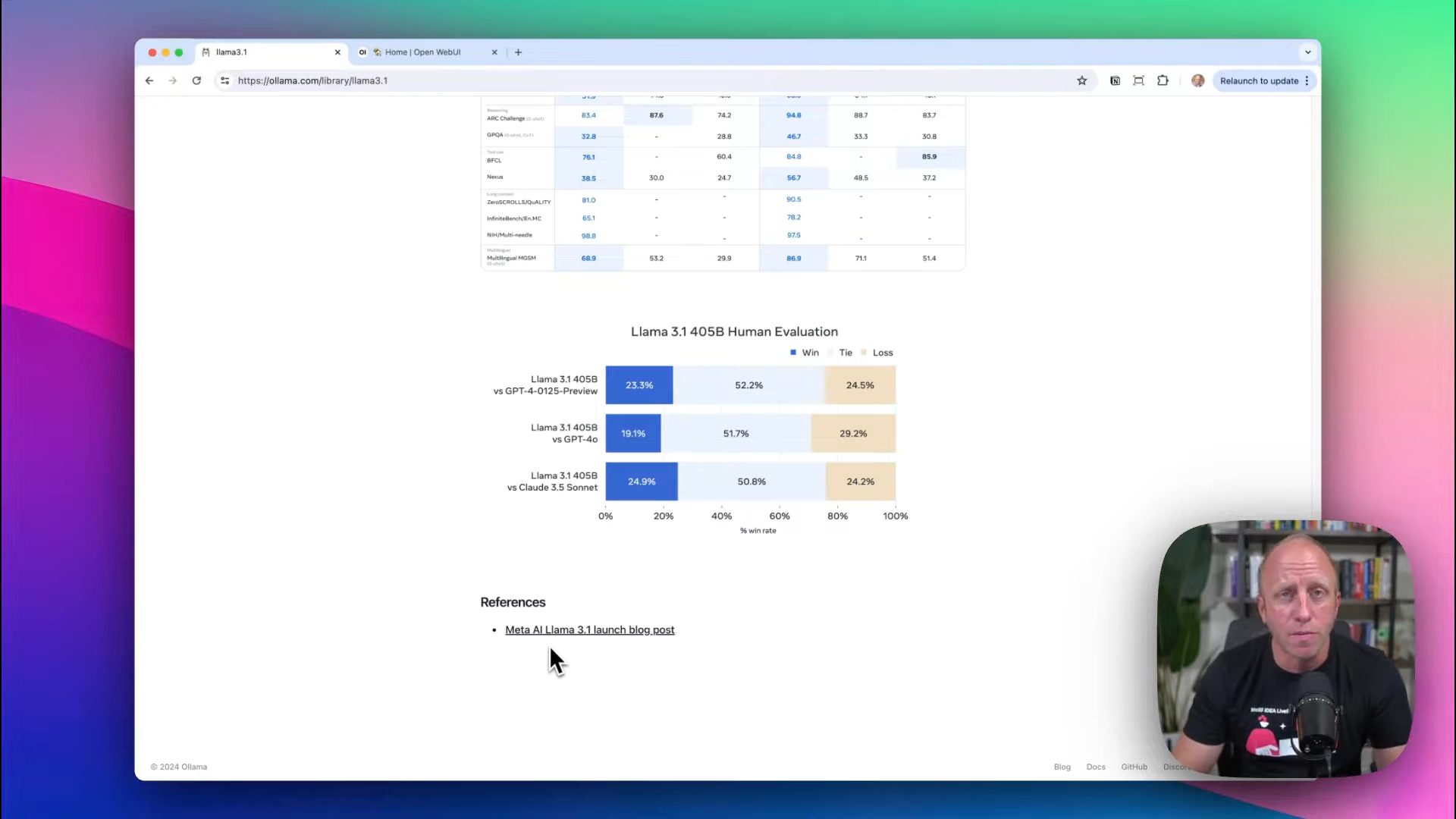
Example with Llama 3.1
For this tutorial, we'll use Llama 3.1, recently released by Meta. It comes in several sizes:
- 8B: 4.7GB
- 70B: 40GB
- 405B: 231GB
Remember, larger models require more storage space and processing power. The 8B model is a great starting point as it doesn't demand hefty resources.
Running the CLI
To run the model, you first need to download it. Here’s a sample command to get you started:
ollama download llama-3.1-8B
After downloading, run the command to initialize the model:
ollama run llama-3.1-8B
Once you run the command, you’ll be prompted to interact with the LLM directly through the CLI, allowing you to send messages and receive responses.
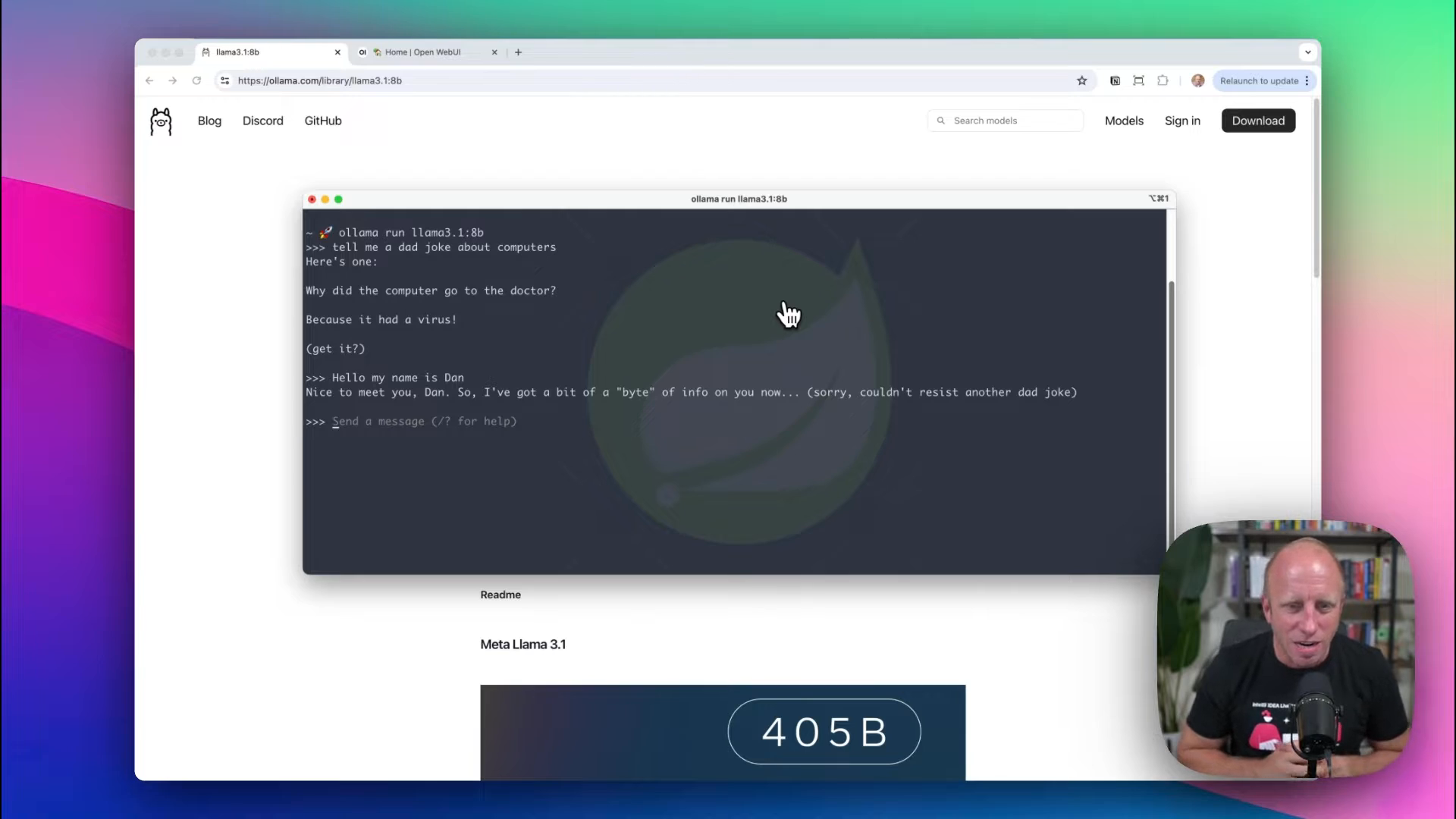
Call the LLM
A fun way to test large language models is through something non trivial, like Dad Jokes. For example, if you ask the model “Tell me a funny dad joke about computers” you might get a response similar to this:
> Why did the computer go to the doctor?> Because it had a virus.
These interactions showcase the LLM’s ability to process and respond to prompts quickly, all done locally.
Enhancing Developer Experience with Open Web UI
While the CLI is great for quick tests, a more robust developer experience can be achieved through a project called Open Web UI. This self-hosted web UI is designed to operate offline and supports various LLM runners, including Ollama.
Setting Up Open Web UI
To get started, ensure you have Docker Desktop installed. With Ollama and Docker set up, run the following command:
docker run -d -p 3000:3000 openwebui/ollama
Check Docker Desktop to confirm that Open Web UI is running. Now, access the UI via http://localhost:3000. You may need to authorize access initially.
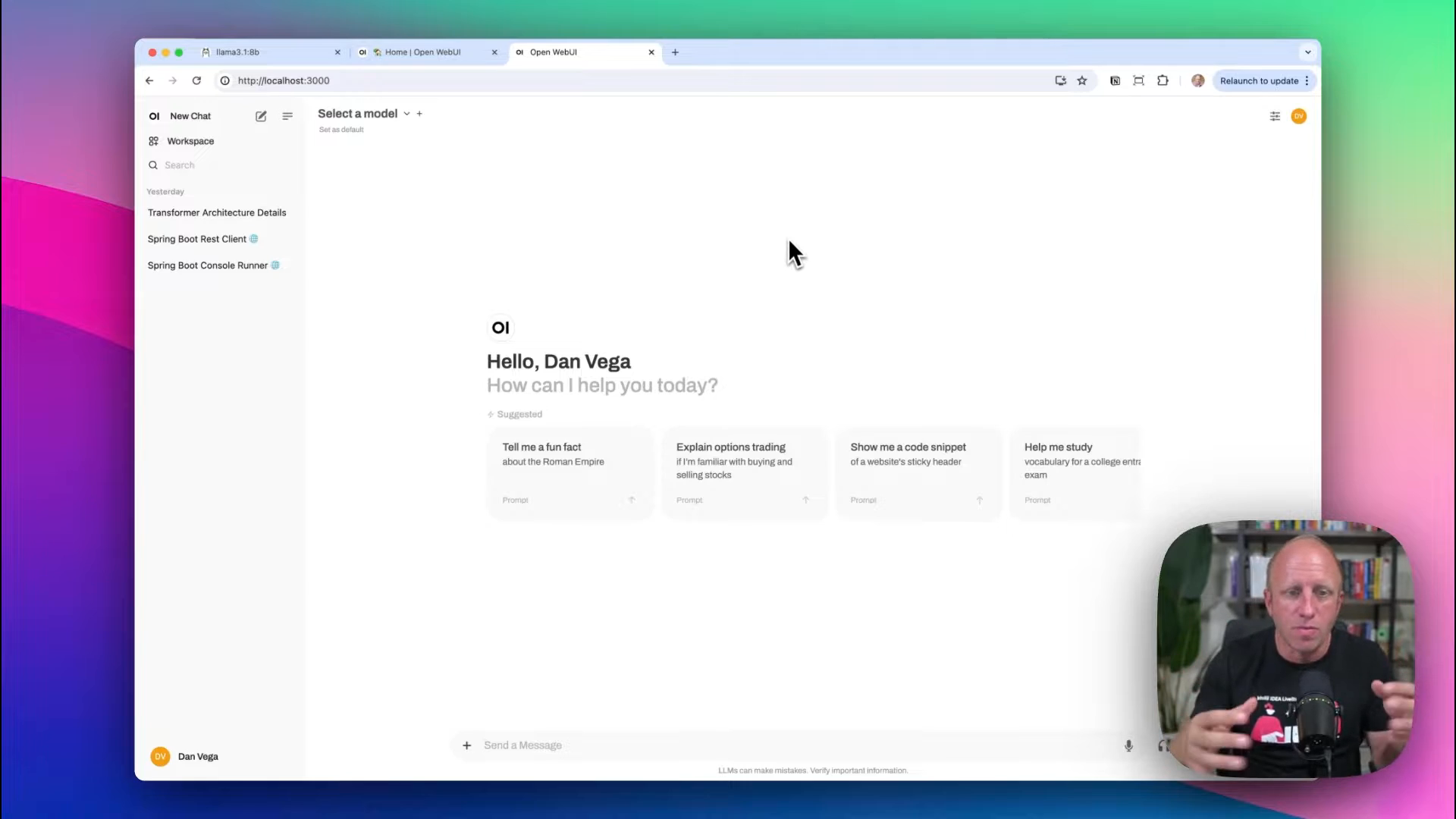
Exploring the UI
Open Web UI offers a familiar interface if you've used applications like ChatGPT. It allows you to manage and interact with multiple models simultaneously, offering features like:
- Model selection
- Contextual conversation history
- Code formatting for better readability
Select the default model (e.g., Llama 3.1) to streamline interactions.
Practical Examples
Conversational Example
Start a chat with something light-hearted, like:
> Tell me a dad joke about dogs.> Why did the dog go to the vet? Because it was feeling a little "ruff."
Coding Example
Now, let's see how it handles code-related tasks:
> What are the best ways to iterate over a list in Java?
The response might include several methods like for-each loop, traditional for loop, iterator, and streams API.
Documentation Usage
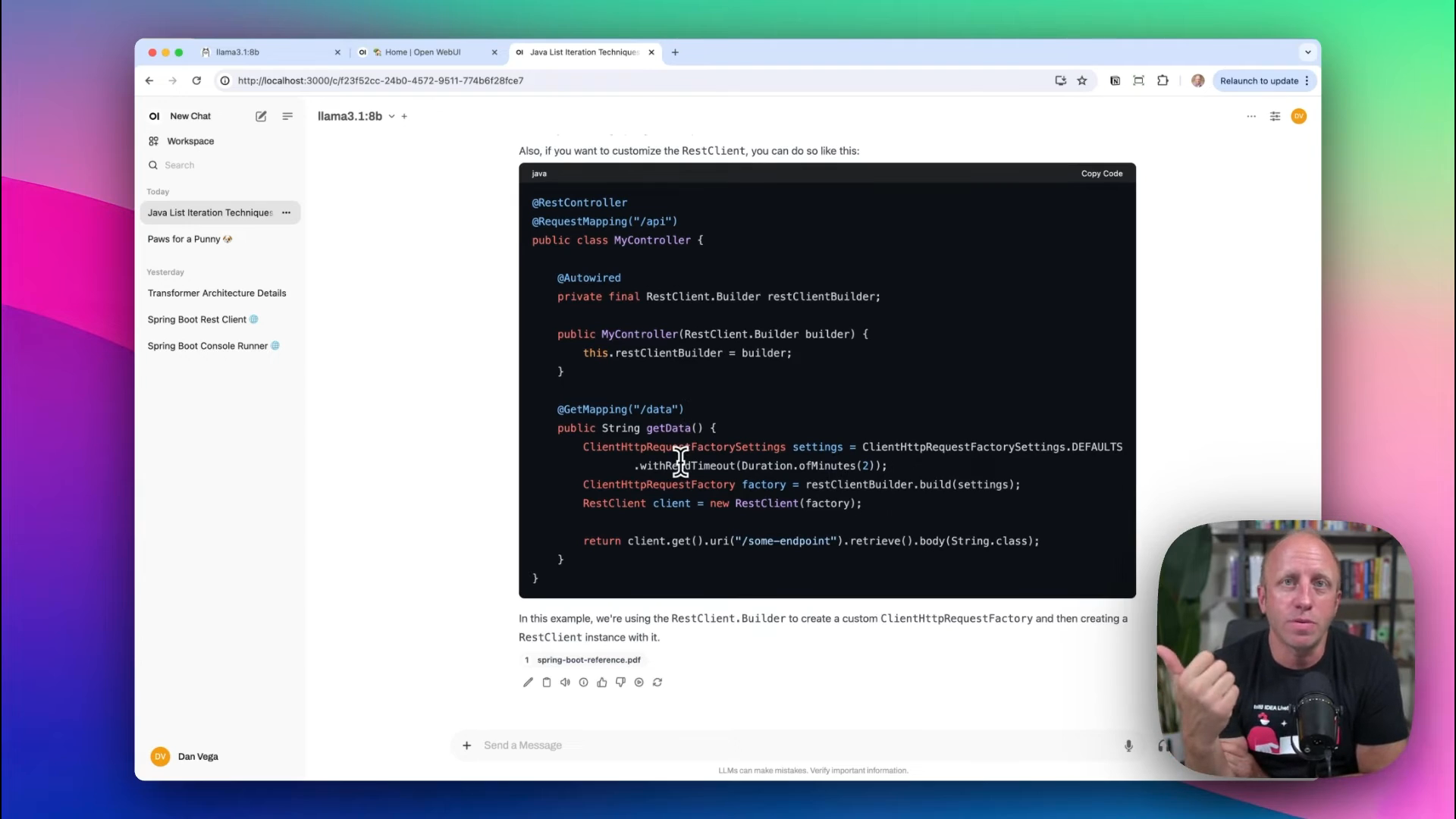
Ollama allows you to upload your own documents for a more tailored response. For instance, if you're working with Spring Boot 3.2, provide relevant documentation:
- Click on
Moreand upload the file. - Re-ask the question relevant to the uploaded docs.
> Give me a code example of how to use the `REST Client` in Spring Boot 3.2.
With the document uploaded, the LLM can now offer accurate and current details, enhancing its utility for your specific needs.
Conclusion
Running large language models locally using Ollama, enhanced with tools like Open Web UI, provides significant advantages in terms of cost and security. The capability to customize interactions with local data makes it a compelling choice for developers and enterprises alike.
"For me, the ability to add my own documents is what really brings this home. It allows customization and privacy that online LLMs can't offer."
As always, happy coding!