Supercharge Your LLM Applications with Model Context Protocol (MCP)
Have you ever been frustrated by the limitations of large language models? Despite their impressive capabilities, LLMs are confined by their training data and knowledge cutoff dates. They can't access real-time information, interact with your local files, or connect to your organization's internal systems - until now.
Enter Model Context Protocol (MCP), a framework that bridges the gap between AI models and external data sources. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore what MCP is, why it matters for Java and Spring developers, and provide detailed instructions on how you can start using it in your applications today.
The Problem: LLM Limitations
Before diving into MCP, let's understand the core problem it solves. Large language models have revolutionized how we interact with AI, but they face significant limitations:
- Knowledge Cutoffs: Models like Claude and ChatGPT only have information up to their training cutoff date. Ask Claude about yesterday's news or a recent software release, and you'll likely get an apologetic response about its knowledge limitations.
- No Access to Real-Time Data: Weather conditions, market prices, sports scores, or current events remain unknown to LLMs without external help.
- No Visibility into Your Systems: LLMs can't access your files, databases, or internal tools by default, limiting their usefulness in enterprise settings.
- Integration Complexity: Building custom connectors for each external service is time-consuming and leads to duplication of effort across teams and organizations.
These limitations create a significant gap between what LLMs can do in theory and what they can deliver in practice, especially in business applications where access to current and private data is essential.
What is Model Context Protocol?
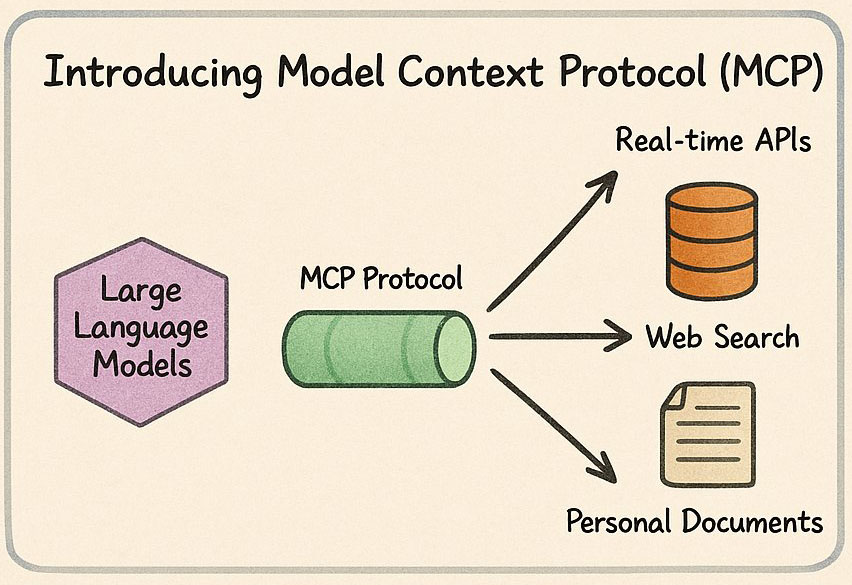
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a standardized framework developed by Anthropic (the makers of Claude) that enables large language models to interact with external tools and data sources. It defines a consistent way for LLMs to communicate with servers that provide access to various capabilities.
Think of MCP as the "USB standard" for AI integrations. Before USB, every device would need a different connector type, creating chaos for users and manufacturers. Similarly, MCP establishes a common protocol for LLMs to connect with external services, eliminating the need for custom integrations for each service and model combination.
The protocol is:
- Open and standardized: Any LLM can implement it, not just Claude
- Secure: It includes built-in security measures like access controls and permission systems
- Extensible: Developers can create servers for any type of data source or tool
- Easy to implement: With SDKs available for multiple languages, including Java
How MCP Works: The Architecture

MCP follows a client-server architecture:
MCP Clients
These are applications that can connect to MCP servers and include:
- Claude Desktop: Anthropic's desktop application for Claude
- Claude Code: A command-line tool for developers
- IDE integrations: Like Cursor and WinSurf
- Custom applications: Your own applications that implement the MCP client protocol
MCP Servers
These are services that implement the MCP protocol to provide specific functionality:
- File system servers: Access to read and write files
- Web search servers: Like Brave Search for accessing current web information
- Database connectors: For querying your organization's data
- API integrations: For connecting to services like GitHub, Slack, or your internal microservices
When a user asks a question that requires external information, the process works like this:
- The user submits a query to the LLM through an MCP-enabled client
- The LLM recognizes it needs external data to answer the query
- The client routes the request to the appropriate MCP server
- The MCP server executes the required operation (file read, web search, API call, etc.)
- The server returns the data to the LLM
- The LLM uses this data to generate a response
This architecture allows LLMs to maintain their core functionality while seamlessly extending their capabilities through the MCP ecosystem.
Why MCP Matters for Java and Spring Developers
What makes MCP particularly exciting for the Java ecosystem is that the official Java SDK for MCP was contributed by the Spring team! This means Java developers can easily build and integrate MCP servers into their Spring applications.
For Spring developers, MCP offers:
- Integration with existing applications: Connect your Spring Boot services to LLMs without major architectural changes
- Familiar development paradigm: Use Spring's dependency injection, configuration, and security features
- Enterprise-grade capabilities: Build robust, scalable MCP servers suitable for production use
- Spring AI integration: Work seamlessly with the Spring AI project for comprehensive AI solutions
The Spring team's involvement in MCP signals the importance of this protocol in the future of enterprise AI integration. By learning MCP now, you're preparing for a significant shift in how businesses will leverage AI capabilities.
Getting Started with MCP: Step-by-Step Guide
Let's walk through a complete example of setting up and using MCP with Claude Desktop. This will give you a practical understanding of how MCP works before we dive into Java-specific implementations in a future tutorial.
Step 1: Install an MCP Client
For this example, we'll use Claude Desktop, which you can download from claude.ai/desktop.
Step 2: Configure an MCP File System Server
The file system server allows Claude to access files on your local machine (with appropriate permissions). Here's how to set it up:
- Ensure you have Node.js installed on your system
- Create a configuration file for Claude Desktop:
- On macOS:
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json - On Windows:
%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
- On macOS:
- Add the following configuration to the file:
{
"mcp_servers": [
"npx @anthropic-ai/mcp-fs --allow-paths=/your/allowed/path"
]
}
Replace /your/allowed/path with the path you want to give Claude access to, such as your Downloads folder.
Step 3: Launch Claude Desktop
Start (or restart) Claude Desktop. If configured correctly, you should see a small plug icon in the interface indicating that MCP servers are connected. Clicking this icon will show you which servers are available.
You'll also see a hammer icon that shows all the MCP tools available to you. The file system server provides tools like:
createDirectorydeleteDirectorygetFileInfolistDirectorymoveFilereadFilewriteFile
Step 4: Test Basic File Access
Try asking Claude questions about your files:
- "How many files are in my Downloads folder?"
- "What's the largest file in my Downloads folder?"
- "List all PDF files in my Downloads folder"
Claude should now be able to access your file system within the allowed paths and answer these questions.
Step 5: Add a Web Search Server
Now, let's add web search capabilities to Claude Desktop:
- Sign up for a Brave API key at brave.com/search/api/
- Update your Claude Desktop configuration file:
{
"mcp_servers": [
"npx @anthropic-ai/mcp-fs --allow-paths=/your/allowed/path",
"npx @anthropic-ai/mcp-brave --api-key=YOUR_BRAVE_API_KEY"
]
}
Replace YOUR_BRAVE_API_KEY with your actual API key.
Step 6: Test Web Search
After restarting Claude Desktop, you can now ask questions that require current information:
- "What are the latest developments in quantum computing?"
- "What's the current weather in New York City?"
- "How many episodes of Daredevil Born Again are available now?"
Claude should now be able to search the web and provide up-to-date answers.
Exploring Available MCP Servers
There are numerous MCP servers already available that you can start using immediately. Here's a selection of popular ones:
1. File System Server
- Purpose: Access to read and write local files
- Installation:
npx @anthropic-ai/mcp-fs --allow-paths=/path/to/access - Use Cases: Document analysis, local file management, working with local datasets
2. Brave Search
- Purpose: Web search capabilities for up-to-date information
- Installation:
npx @anthropic-ai/mcp-brave --api-key=YOUR_API_KEY - Use Cases: Current events, research, finding recent information outside the LLM's knowledge cutoff
3. GitHub Server
- Purpose: Access to GitHub repositories, issues, and pull requests
- Installation:
npx @anthropic-ai/mcp-github --token=YOUR_GITHUB_TOKEN - Use Cases: Code analysis, repository management, issue tracking
4. Google Calendar
- Purpose: Access to Google Calendar events and schedules
- Installation: Available through various third-party implementations
- Use Cases: Schedule management, meeting planning, time tracking
5. Slack Integration
- Purpose: Access to Slack channels and messages
- Installation: Available through various third-party implementations
- Use Cases: Team communication, message analysis, workflow automation
6. Database Connectors
- Purpose: Access to various database systems
- Installation: Available through various third-party implementations
- Use Cases: Data analysis, reporting, information retrieval
These are just a few examples of the growing ecosystem of MCP servers. You can find more at the MCP Server Directory or through community resources like GitHub.
Real-World Use Cases for MCP
MCP opens up numerous possibilities for applications:
- Customer support bots: Access CRM data to provide personalized support
- Internal knowledge bases: Search company documentation and wikis
- Development assistants: Help developers by accessing code repositories, CI/CD systems, and issue trackers
- Data analysis tools: Access and analyze company data in real-time
- Administrative assistants: Manage calendars, emails, and internal systems
- Document processing: Extract, analyze, and process information from company documents
Example Scenario: Development Assistant
Imagine a development assistant powered by Claude with MCP access to:
- Your GitHub repositories
- Your Jira issue tracker
- Your CI/CD pipeline
- Your internal documentation
With these connections, you could ask questions like:
- "What open issues are assigned to me?"
- "Show me the failed tests from the last build"
- "Help me understand how our authentication service works"
- "What code changes were made to the payment module last week?"
The assistant could pull this information in real-time, providing you with accurate and contextual responses that would be impossible with a standard LLM.
Best Practices for Using MCP
When working with MCP, consider these best practices:
- Security First: Only connect to trusted MCP servers and be mindful of the permissions you grant
- Clear User Permissions: Always make it clear to users what access is being granted to the LLM
- Path Restrictions: Limit file system access to specific directories to prevent accidental exposure
- API Rate Limits: Be aware of rate limits when using services like web search or GitHub
- Error Handling: Prepare for scenarios where MCP servers might be unavailable or return errors
- Data Privacy: Be cautious about what information you allow the LLM to access
- Testing: Thoroughly test MCP integrations before using them in production
Looking Forward: The Future of MCP
MCP is still in its early stages, but it's rapidly evolving. Here's what we can expect in the future:
- Expanded Ecosystem: More MCP servers covering additional services and data sources
- Enterprise Adoption: Increased use in business applications and workflows
- Standards Development: Further refinement of the protocol and security standards
- Integration with Development Tools: Deeper integration with IDEs and development workflows
- Cross-Model Compatibility: More LLMs supporting the MCP standard
In upcoming posts, we'll explore how to build your own MCP servers using Java and Spring, diving deep into the implementation details and best practices.
Conclusion
Model Context Protocol represents a significant advancement in making AI more integrated and useful within our software systems. For Java and Spring developers, MCP offers a standardized way to connect LLMs with our applications, data sources, and services.
By learning and implementing MCP today, you'll be positioned to create more capable and context-aware AI-powered applications. The protocol is rapidly becoming the standard for AI integration, and its adoption will only accelerate.
Resources to Continue Your MCP Journey
- Official MCP Documentation: Visit modelcontextprotocol.io for comprehensive documentation.
- Spring AI GitHub Repository: Check out the Spring AI project which includes MCP support.
- MCP Server Directory: Browse available MCP servers at modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/examples/servers.
- Java SDK Documentation: Review the Java SDK for MCP contributed by the Spring team.
- Claude Developer Documentation: Explore the Claude API docs for more information on Claude integration.
In my next tutorial, we'll show you how to build your own MCP servers using Java and Spring, allowing you to create custom integrations for your specific use cases. Stay tuned!
Are you excited about implementing MCP in your projects? What types of integrations would be most valuable for your use cases? Let me know in the comments below!
Happy coding!